At NAH, some of our orthopedic surgeons have additional specialized training in diagnosis and treatment of the bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, tendons, nerves and skin surrounding the foot area. These surgeons use medical, physical and rehabilitative methods, as well as surgery, to treat patients of all ages and walks of life.
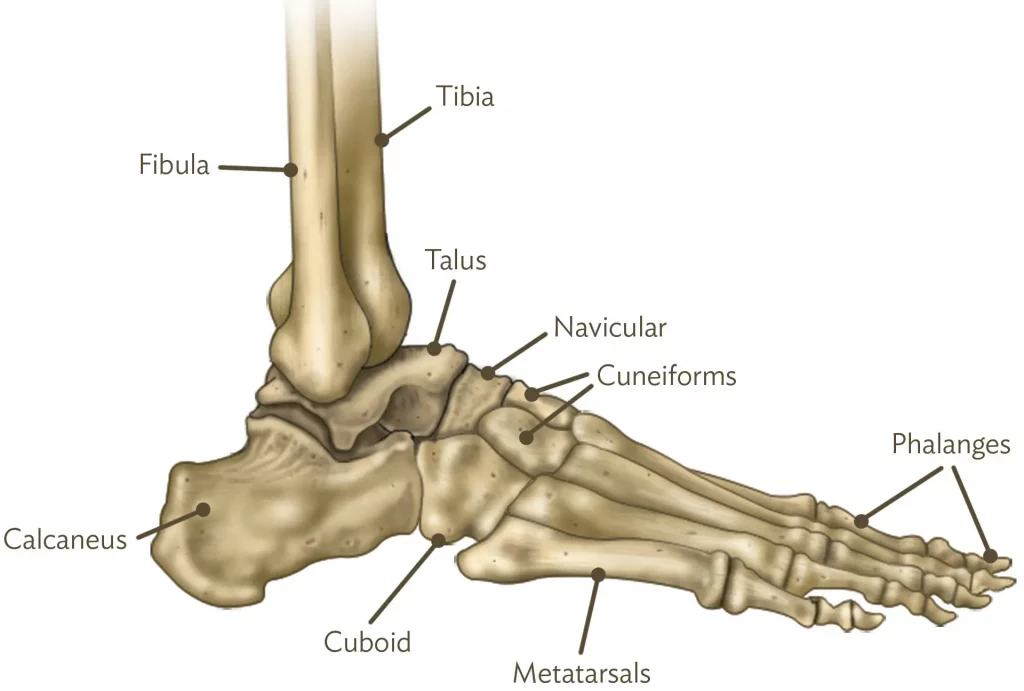
The ankle joint is made up of three bones – the tibia (shinbone), the fibula (a smaller bone of the lower leg) and the talus (a small bone that sits between the heel bone, or calcaneus, and the tibia and fibula).
During the past 30 to 40 years, doctors have noted an increase in the number and severity of broken ankles, due in part to an active, older population of “baby boomers.” Because a severe ankle sprain can feel the same as a broken ankle, every ankle injury should be evaluated by a physician.
Multiple diseases can contribute to foot and ankle issues. Diabetic foot problems are a major health concern and are a common cause of hospitalization. Most foot problems that people with diabetes face arise from two serious complications of the disease: nerve damage and poor circulation.
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often starts in the small joints of the hands and feet, and usually affects the same joints on both sides of the body. More than 90 percent of people with RA develop symptoms in the foot and ankle over the course of the disease.
Too much weight also can seriously impact the growth and health of bones, joints, and muscles.
Source: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
